Python_Day 7
Python Day 7_Beginner – Hangman
How to break a complex problem down into a flow chart (Flow chart programming)
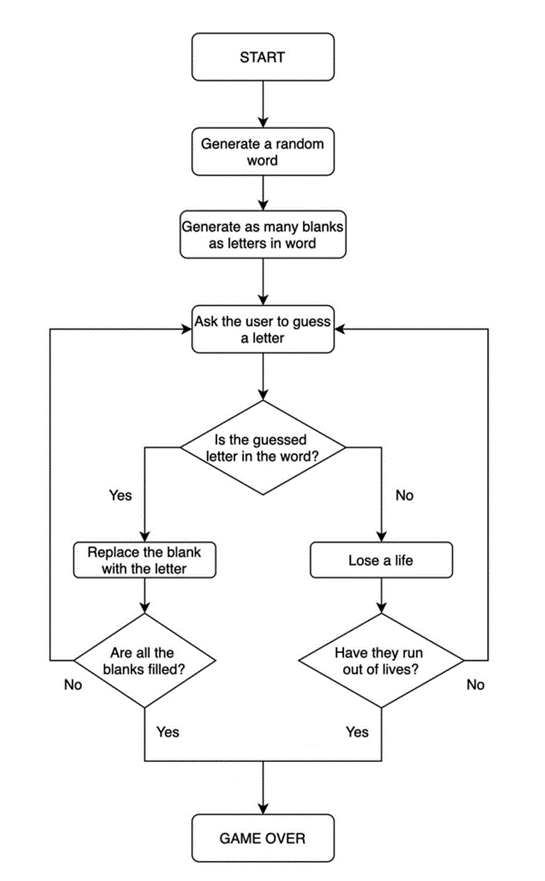
Challenge 1 – Picking a random word and checking
import random
#step 1
#TODO-2 - Ask the user to guess a letter and assign their answer to a variable called guess. Make guess lowercase.
guess = input("Guess a letter: ").lower()
#TODO-3 - Check if the letter the user guessed (guess) is one of the letters in the chosen_word.
# for letter in chosen_word:
# if letter == guess:
# print("Right")
# else:
# print("Wrong")
Challenge 2 – Replacing Blanks with guesses
#step 2
#TODO-1: - Create an empty List called display.
#For each letter in the chosen_word, add a "_" to 'display'.
#So if the chosen_word was "apple", display should be ["_", "_", "_", "_", "_"] with 5 "_" representing each letter to guess.
display = []
word_length = len(chosen_word)
for _ in range(word_length):
display += "_"
#TODO-2: - Loop through each position in the chosen_word;
#If the letter at that position matches 'guess' then reveal that letter in the display at that position.
#e.g. If the user guessed "p" and the chosen word was "apple", then display should be ["_", "p", "p", "_", "_"].
for position in range(word_length):
letter = chosen_word[position]
if letter == guess:
display[position] = letter
#TODO-3: - Print 'display' and you should see the guessed letter in the correct position and every other letter replace with "_".
#Hint - Don't worry about getting the user to guess the next letter. We'll tackle that in step 3.
print(display)
Challenge 3 – Checking if the player has won
#step3
#TODO-1: - Use a while loop to let the user guess again. The loop should only stop once the user has guessed all the letters in the chosen_word and 'display' has no more blanks ("_"). Then you can tell the user they've won.
#add the following infront of guess variable
end_of_game = False
while not end_of_game:
#add after display variable
if "_" not in display:
end_of_game = True
print("You Win")
Challenge 4 – Keeping track of the player’s lives
#step 4
#TODO-1: - Create a variable called 'lives' to keep track of the number of lives left.
#Set 'lives' to equal 6.
lives = 6
# TODO-2: - If guess is not a letter in the chosen_word,
# Then reduce 'lives' by 1.
# If lives goes down to 0 then the game should stop and it should print "You lose."
if guess not in chosen_word:
lives -= 1
if lives == 0:
end_of_game = True
print("You lose")
#step 4
#TODO-3: - print the ASCII art from 'stages' that corresponds to the current number of 'lives' the user has remaining.
import Hangman_art
print(Hangman_art.stages[lives])
Challenge 5 – Improving the User Experience (Using module)
#step 5
#TODO-1: - Update the word list to use the 'word_list' from hangman_words.py
import hangman_word_list
chosen_word = random.choice(hangman_word_list.word_list)
#step 5
#TODO-3: - Import the logo from hangman_art.py and print it at the start of the game.
from Hangman_art import logo
print(logo)
#step5
# TODO-4: - If the user has entered a letter they've already guessed, print the letter and let them know.
if guess in display:
print(f"You've already guessed {guess}")
# step 5
# TODO-5: - If the letter is not in the chosen_word, print out the letter and let them know it's not in the word.
print(f"You guessed {guess}, that's not in the word. You lose a life")
Hangman Code
import random
import hangman_word_list
chosen_word = random.choice(hangman_word_list.word_list)
lives = 6
from Hangman_art import logo
print(logo)
display = []
word_length = len(chosen_word)
for _ in range(word_length):
display += "_"
end_of_game = False
while not end_of_game:
guess = input("Guess a letter: ").lower()
if guess in display:
print(f"You've already guessed {guess}")
for position in range(word_length):
letter = chosen_word[position]
if letter == guess:
display[position] = letter
if guess not in chosen_word:
print(f"You guessed {guess}, that's not in the word. You lose a life")
lives -= 1
if lives == 0:
end_of_game = True
print("You lose")
print(display)
if "_" not in display:
end_of_game = True
print("You Win")
import Hangman_art
print(Hangman_art.stages[lives])